Some of the Important Points to Consider About the Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations and Mechanism of AWS

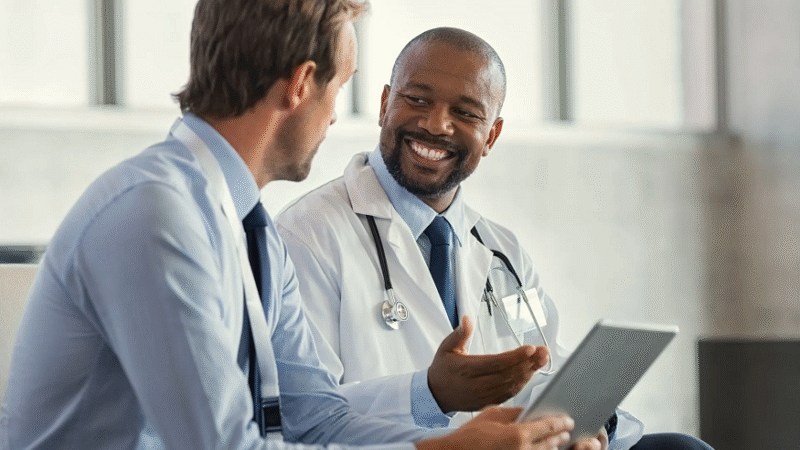
Alcohol withdrawal (AW) can occur in heavy drinkers who suddenly cut back on alcohol consumption or completely abstain. Signs and side effects of AW can incorporate, among others, gentle to direct quakes, crabbiness, uneasiness, or disturbance. Delirium tremens, hallucinations, and seizures are the most severe withdrawal symptoms. In the absence of alcohol, excessive neuronal activity is caused by alcohol-induced imbalances in the brain’s chemistry. The treatment of withdrawal symptoms using both pharmacological and nonpharmacological methods is part of the comprehensive assessment of the severity of the patient’s symptoms and any underlying conditions. Outpatient and inpatient treatment options are available. The patient’s recovery can begin with the recognition and treatment of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms.
Points to Ponder
- More than one and a half million people in the United States either enter treatment for alcoholism or are admitted to a general hospital each year due to the medical consequences of alcohol dependence.
- Alcohol withdrawal (AW) affects these patients and a significant number of others who quit drinking without seeking treatment.
- A clinical syndrome known as AW affects people who are accustomed to drinking alcohol regularly but either cut back or stop drinking altogether.
- The central nervous system (CNS) in these individuals has adapted to the constant presence of alcohol in the body and compensates for alcohol’s depressant effects on brain function and nerve cell communication.
- As a result, withdrawal syndrome occurs when the alcohol level suddenly drops because the brain remains hyperactive, or hyperexcited.
Clinical Indicators of Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome
The clinical manifestations and severity of AW syndrome vary significantly between alcoholics. These signs and symptoms can be anything from mild insomnia to severe consequences like delirium tremens (DT) and even death. The frequency with which various drinkers experience symptoms also varies significantly. Some people who drink frequently never experience any signs of alcohol withdrawal. In contrast, withdrawal symptoms in some alcoholics can occur at blood alcohol concentrations (BACs) that would be intoxicating to non-alcohol-dependent individuals but represent a decrease from their usual BACs for dependent patients.
Apparatuses of Alcohol Withdrawal
An early study of men who received large daily doses of alcohol supported the hypothesis that withdrawal in dependent patients occurs as a result of “insufficient” alcohol intake or abstinence rather than nutritional deficiencies. The well-nourished study participants consumed up to 30 standard drinks per day for up to three months. Whenever these men stopped drinking alcohol, they always experienced withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, AW symptoms were dose-dependent: The men who had consumed the most alcohol experienced the most severe withdrawal symptoms, including hallucinations, seizures, and DTs.